Why you should stake and how Finoa supports institutional needs
Table of Contents
Over the past years, we have watched staking emerge as a defining trend in the wider crypto-ecosystem — staking has become the prevailing consensus mechanism for new blockchains and also an increasing interest of institutional investors and corporations.
Navigating the staking landscape is not a straightforward task, however, and its complexity poses a considerable barrier to entry for many investors watching the developments from the sidelines. As interesting as they may seem, Proof of Stake networks vary in nature, and caution is advised when assessing the many opportunities in the space.
Consequently, it is critical that investors and protocols looking to enable and engage in Proof of Stake network participation do their necessary due diligence and identify the right partners to reduce risks and deliver successful outcomes.
In this article we decipher staking in an institutional context, examining how it can serve as an opportunity for investors seeking out passive income from idle assets. We outline how Finoa is working on solutions to bridge investors and blockchain networks, allowing for network participation without compromising decentralization or asset security.
What is the 'Proof of Stake' consensus mechanism?
A blockchain is a record of account balances and transactions that participants share with each other. Distributing this record of previous transactions is simple enough, but the participants also need a way to determine amongst themselves whether new transactions are legitimate or not. An example of an illegitimate transaction is a “double-spend”, whereby a participant attempts to send the same set of tokens to two different places. When the blockchain participants verify that a transaction is legitimate and add it to the blockchain, we say that the participants have “achieved consensus”. The first blockchains used the mechanism of “Proof of Work” to achieve consensus, while many newer blockchains use “Proof of Stake” to achieve consensus. In both blockchain consensus mechanisms, participants are incentivized to verify legitimate transactions and are disincentivized from attempting to verify illegitimate transactions.
In a Proof of Work consensus model, transactions can only be verified after a certain amount of computation effort, or “work”, has been undertaken. For a bad actor to be able to verify his own illegitimate transactions and build a “false” version of the blockchain, he would have to consistently put in more computational work than the other participants, which would require a massive investment in computing hardware and electricity — it’s not impossible, it’s just not worth doing.
In a Proof of Stake consensus model, participants wanting to verify transactions must put their money where their mouth is, literally putting their assets “at stake” to lend credibility to a transaction. If there is any disagreement between participants about the legitimacy of transactions, or if a participant has otherwise broken the rules of the blockchain, some or all of his “staked” tokens are taken away as a punishment. This mechanism is a disincentive for fraudulent behavior and behavior that does not adhere to the rules and standards set forth by the blockchain protocol for verifying transactions.
Is staking crypto safe?
The genius of the original Proof of Work blockchains like Bitcoin was that they not only contained mechanisms for achieving consensus, but also economic incentives for participants to help verify transactions. Every time a participant puts in enough computational work to verify a block full of new transactions, they are rewarded with newly created tokens (hence we call these participants “miners”). This simple mechanism ensures that there are always miners working to verify transactions, protecting the blockchain from double-spending attacks and collecting a reward for the effort.
Proof of Stake blockchains incentivize the verification of transactions in a similar way to Proof of Work. A key difference is that in Proof of Stake, all that is required to help verify transactions is a number of tokens being “staked” on the blockchain — no specialized computing hardware is required. This means that any investment in Proof of Stake tokens can earn a passive return over time if those tokens are being staked on the blockchain.
What are the benefits of staking crypto?
Because Proof of Stake relies only on a number of tokens being allocated to a specific purpose on the blockchain, it does not require high consumption of electricity the way that mining on a Proof of Work blockchain does. This means that Proof of Stake blockchains require less energy consumption than their Proof of Work counterparts.
Another effect of Proof of Stake’s low energy consumption is the potential for greater geographic decentralization. On a global scale, mining with Proof of Work is the most profitable where energy can be had for the lowest cost, resulting in increasingly large mining centers in locations with an abundance of cheap electricity.
Finally, Proof of Stake blockchains hopes to eventually become more “scalable” than their Proof of Work counterparts: supporting more simultaneous transactions without making significant sacrifices in security or decentralization. This is where a great deal of innovation is happening today, and indeed a challenge that blockchains will have to overcome if they are ever to become widely used on a global scale.
Who are staking validators? Should you delegate tokens to them?
In a Proof of Stake blockchain, any participant can stake their tokens and help to verify new transactions, earning a reward in the process. New transactions are bundled together into a block, and once the block is verified, those transactions are officially added to the blockchain. Each block is verified by a single participant, and that participant receives the entire reward for the verification of that block. A random process decides which participant will verify the next block and earn rewards, but a participant with more tokens at stake is more likely to succeed for any given block.
This means that participants with relatively few tokens being staked are unlikely to be able to verify any blocks on a given day. In order for participants with small amounts of tokens to have a chance at verifying blocks and earning a reward, they can pool their tokens together and choose a single participant to verify blocks by staking the entire token pool. This is referred to as “delegating” tokens to a specific “validator”. The validator typically takes a share of the rewards in return for setting up and running the node infrastructure.
While everyone is typically allowed to set up and run their own node infrastructure, we often see that institutional investors choose to delegate staking and partner up with infrastructure experts offering institutional-grade staking-as-a-service offerings. These service providers increase the ease with which participants can participate in staking, and offer institutional token holders the possibility to stake on reliable, secure, and trustworthy infrastructure.
Managing risks from staking crypto
The Proof of Stake mechanism operates on the model that blockchain participants put their tokens at stake to declare the truthfulness of transactions, and are disincentivized from engaging in malicious behavior under the threat of losing some or all of those staked tokens. This punishment is called “slashing”. Even honest and truthful validators, however, need to comply with certain requirements to avoid having tokens slashed, namely that the validator stays continuously connected to the blockchain and verifies transactions exactly in accordance with the blockchain’s rules.
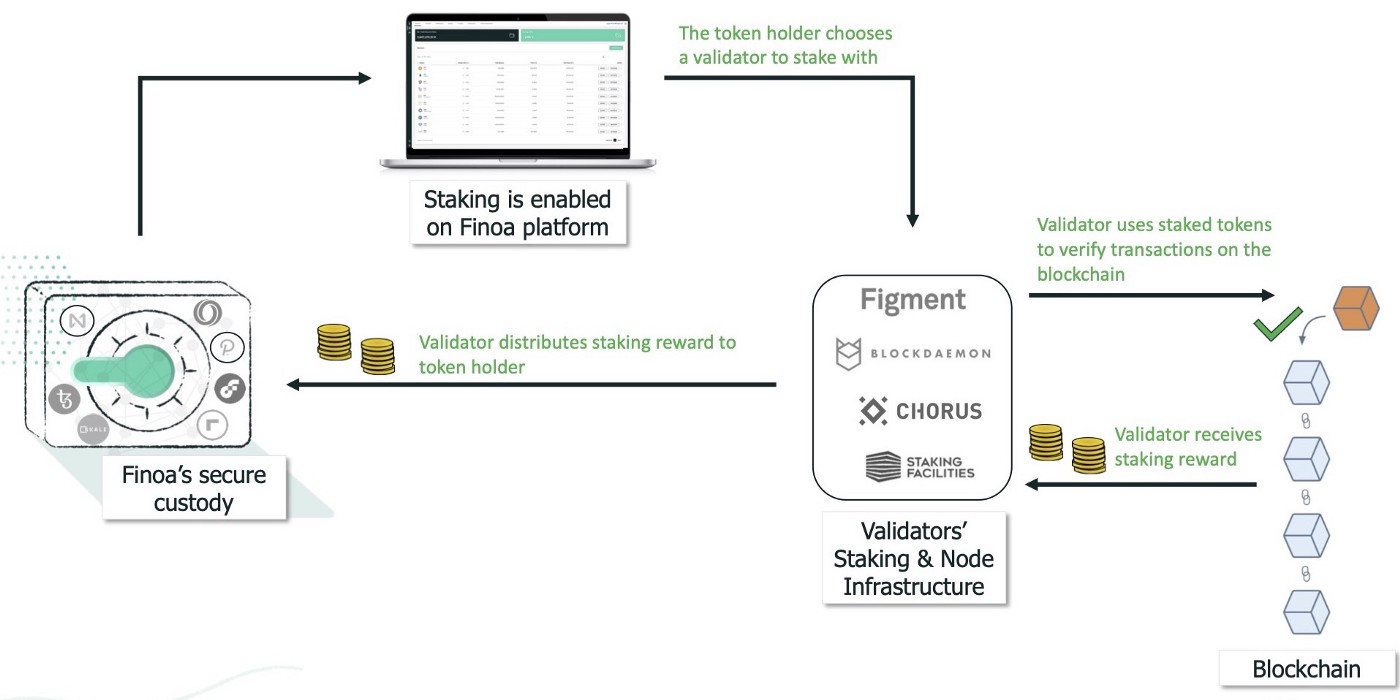
As such, participants should ensure that the validator staking their coins adheres to the highest operational standards and is a fully secure provider. At Finoa, we work with industry-leading validators who are known to have a robust and reliable infrastructure and offer institutional grade staking-as-a-service. We offer investors the choice of several validators to stake with and Tokenholders can delegate their stake to these validators without ever leaving the Finoa platform.
Related article: How to manage crypto risks as a professional investor
Is it possible to stake assets under custody?
Validators do not need to take custody of tokens in order to stake them. When staking with a validator on the Finoa platform, the tokens remain safely inside Finoa’s custody. Investors do not have to take custody of their tokens or navigate the interfaces of third parties — they can stake their tokens safely within the Finoa platform. This presents a unique opportunity for institutional investors looking to earn a passive return on their investments while supporting the blockchains they believe in, all from within an institutional-grade custody solution.
Is the staking experience the same for all blockchain protocols on Finoa?
The implementation of Proof of Stake differs from blockchain to blockchain: some blockchain protocols mandate that tokens be staked for a minimum amount of time, others allow tokens to be “unstaked” at any point but require a length of time to pass before the tokens can be moved again. (These amounts of time are measured in “epochs”, which may be a certain number of hours, days, or weeks.) Likewise from blockchain to blockchain, there will be differences in the rate at which staking rewards are accumulated, how these rewards are distributed, and how often.
Finoa supports decentralization - Users can choose from various staking-as-a-service providers
At Finoa, we understand the importance of decentralization and the counterproductivity of a large number of a blockchain’s tokens being staked with a single validator. Thus, we aspire to give clients a choice of several validators to stake with, making it less likely that a single validator will begin to dominate a blockchain. Our clients are free to choose from a selection of institutional-grade staking-as-a-service providers that we have carefully selected. It is even possible for clients to stake different portions of their tokens with different validators, all from within the Finoa platform.
In other words, our role is that of a bridge, connecting institutional token holders to institutional-grade validators. We currently work with leading staking-as-a-service providers and support in-demand Proof of Stake protocols and their native tokens.
While it’s becoming more common to see cryptocurrency brokers and exchanges offer staking, very few platforms offer their users an open selection of prime validators. Indeed the user is usually not provided with any information at all about the validator infrastructure that their tokens are being staked on, failing to satisfy the safety and security concerns of larger institutional customers.
Current challenges and future aspirations for institutional staking
A great deal of innovation is happening today as blockchain protocols explore implementations of the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism. New blockchain designs codify unique innovations or differences in philosophy, and Finoa is always looking for opportunities to integrate with new and exciting protocols. We aim to continue adding partners to our platform, giving institutional investors and corporations access to the diverse world of digital assets — this includes launches of completely new protocol mainnets as well as the addition of new tokens on existing base layer blockchains.
Our highest priority will always be ensuring the safety and security of our client's digital assets, and this focus determines which staking validators we choose to work with. We also remain committed to supporting decentralization by allowing clients to choose from several institutional-grade validators.
At Finoa we pride ourselves on having the technical flexibility and agility required to keep up with constantly evolving blockchain protocols, and we aspire to be the custodian of choice for institutional investors seeking a bridge into the world of digital assets and a way to put their tokens to work by earning staking rewards.
If you are interested in learning more about our current offerings and future integration roadmap, please reach out to us directly here.